
In the third case, the thermal energy gets concentrated into a smaller volume as the gas contracts. In the first two examples, thermal energy (dispersed) gets concentrated into organized kinetic energy of a macroscopic object- a book, a propeller. What do all these scenarios that conform to the First Law but are nevertheless never seen to occur have in common? In every case, energy becomes less spread out, less "diluted". (To the extent that air behaves as a perfect gas, this doesn't involve the First Law at all.)
Because motion of the air molecules is completely random, there is no reason why all of the molecules in one half of a room cannot suddenly "decide" to move into the other half, asphyxiating the unfortunate occupants of that side. 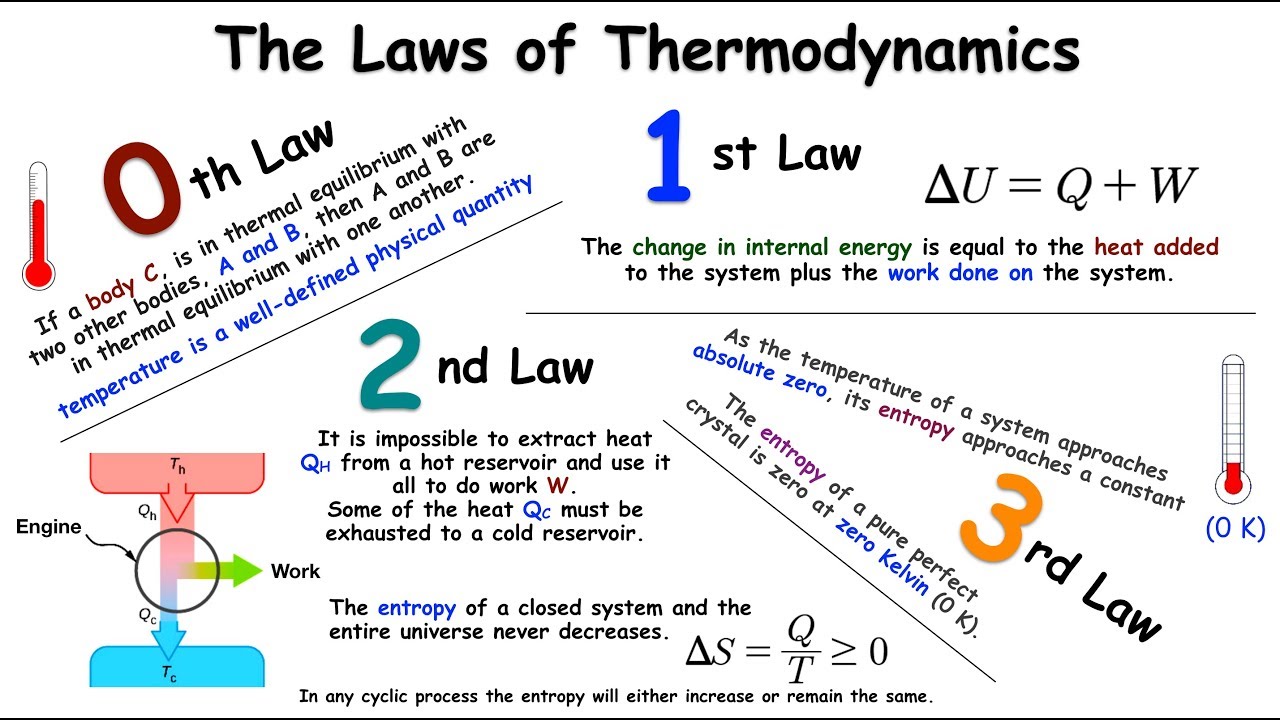
As long as the work done to turn the propeller is no greater than the heat required to melt the ice, the First Law is satisfied.
One might propose a scheme to propel a ship by means of a machine that takes in seawater, extracts part of its thermal energy which is used to rotate the propeller, and then tosses the resulting ice cubes overboard. Similarly, why can't the energy imparted to the nail (and to the wood) by a hammer not pop the nail back out? According to the First Law, there is no reason why placing pre-warmed book on a warmed table top should not be able to propel the book back into the air. 
The kinetic energy contained in the falling book is dispersed as thermal energy, slightly warming the book and the table top.
Suppose you drop a book onto a table top. The significance of this law is that it tells us that any proposed process that would violate this condition can be dismissed as impossible, without even inquiring further into the details of the process.įor simple mechanical operations on macroscopic objects, the First Law, conservation of energy, is all we usually need to determine such things as how many joules of energy is required to lift a weight or to boil some water, how many grams of glucose you must metabolize in order to climb a hill, or how much fuel your car needs to drive a given distance.īut if you think about it, there are a number of "simple mechanical operations" that never occur, even though they would not violate energy conservation. The First Law of thermodynamics, expressed as Δ U = q + w, is essentially a statement of the law of conservation of energy. According to the Second Law of Thermodynamics, complete conversion of heat into work by a spontaneous cyclic process is impossible. The fraction of heat that can be converted into work is limited by the fall in temperature between the input to the engine and the exhaust. A heat engine is a device that converts heat into work. #Quizlet second law of thermodynamics simple states that free#
Processes that do not exchange heat with the surroundings (such as the free expansion of a gas into a vacuum) involve entropy change of the system alone, and are always spontaneous. 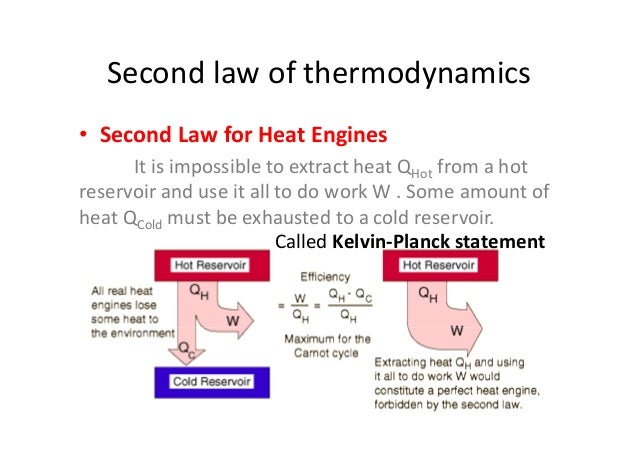 In any macroscopic change, the entropy of the world (that is, system + surroundings) always increases it never decreases. You are expected to be able to define and explain the significance of terms identified in green type.
In any macroscopic change, the entropy of the world (that is, system + surroundings) always increases it never decreases. You are expected to be able to define and explain the significance of terms identified in green type.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
